WHITEPAPER

There are various challenges that make calibrating radio frequency test probes demanding. The goal is to provide virtually error-free RF tests while optimising the simplicity, speed, and cost of testing. This will become increasingly important when, for example, the introduction of 5G means working and testing with higher frequencies.
Based on these requirements INGUN customers should decide which calibration / compensation method is best suited for their application when designing the test system. Our white paper presents various methods, which provide a wide range of possibilities from simple calibrations to very complex calibrations.
The more elaborate the calibration, the more accurate the measurement result in the series test. However, the most complicated calibration procedure is not always necessary; often a simpler procedure is sufficient to optimise the measurement result and reduce errors. In addition to errors that arise due to the shortcomings of commonly used calibration kits, there are two main errors that typically arise when calibrating an RF probe:
- The positioning error: this occurs when the RF probe is not exactly aligned with the test point.
- The calibration path error: this occurs when extensions are added or removed after the calibration has been performed.
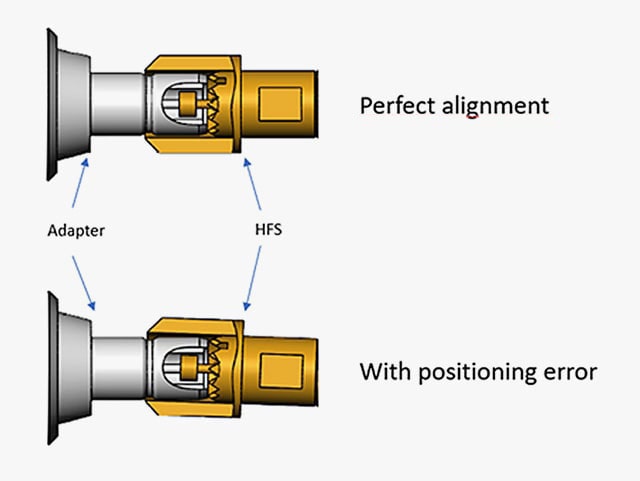
Using the appropriate calibration method for the application in question, errors can be avoided altogether. In our white paper, we illustrate various calibration methods and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each.
